Politics
F-16 Fighting Eagle vs. Gripen E: A Clash of Fighter Jets
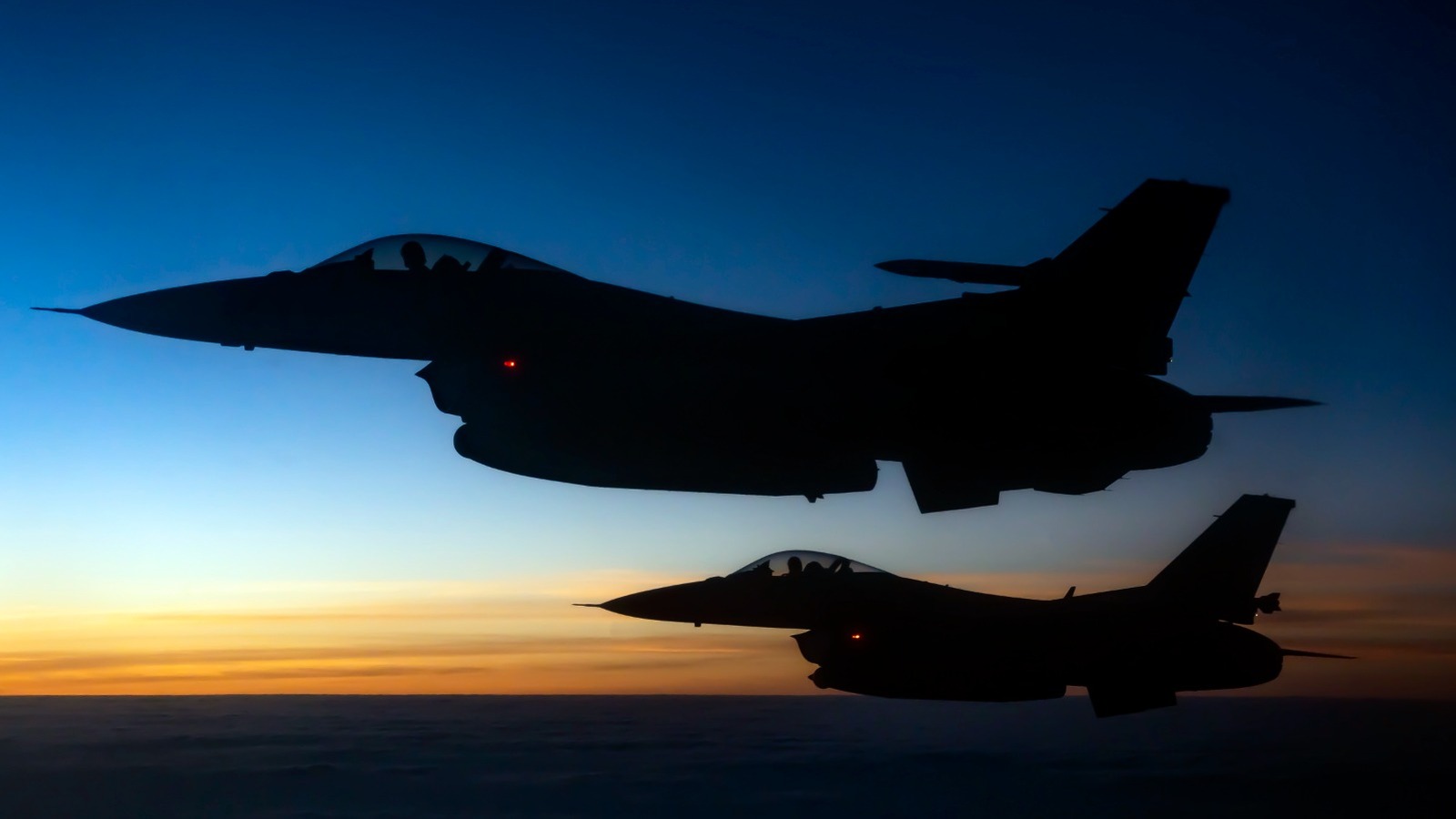

The debate over the capabilities of fighter jets often centers on two formidable contenders: the F-16 Fighting Eagle and the SAAB Jas 39 Gripen. Both aircraft serve as lightweight, multi-role fighters for their respective nations—the United States and Sweden. The newest variants, the F-16 Block 70/72 and the Gripen E, showcase distinct characteristics that highlight their unique advantages.
The F-16 Fighting Eagle, produced by Lockheed Martin, has been a key part of the U.S. Air Force since its introduction in 1979. This single-engine jet is widely recognized for its versatility and combat performance. By contrast, the Gripen E, developed by Swedish manufacturer SAAB, emphasizes a multi-role capability that allows it to excel in various mission types.
Design and Performance Differences
Visually, the two jets present notable differences. The Gripen E features a cropped delta-wing design and canards positioned near its cockpit, enhancing its agility. In contrast, the F-16 has a traditional single air intake located beneath the cockpit. The Gripen is powered by the General Electric F414-GE-39E turbofan engine, which generates approximately 22,000 pounds of thrust, allowing it to reach speeds approaching Mach 2. The F-16’s engine options vary between the Block 70, which utilizes the General Electric F110-GE-129, and the Block 72, equipped with the Pratt & Whitney F100-PW-229, both capable of producing around 29,000 pounds of thrust and exceeding speeds of 1,500 mph.
Weight plays a crucial role in a fighter’s combat effectiveness. The F-16 has a maximum weight of 20,300 pounds when empty, while the Gripen E weighs in at approximately 17,600 pounds. This difference in weight contributes to their maneuverability, with the lighter Gripen often having an advantage in agility during dogfights.
Armament and Versatility
Armament is essential for any modern fighter jet. The F-16 is equipped with an M61A1 20mm Vulcan rotary cannon, while the Gripen E features a 27 mm Mauser BK-27 cannon. Both aircraft are designed with multiple hardpoints for various weapons configurations. The F-16 has a total of 11 external hardpoints, one more than the Gripen E, allowing for a broader range of weapons, including beyond-visual-range missiles.
Moreover, the F-16’s higher maximum takeoff weight—approximately 48,000 pounds—enables it to carry larger munitions compared to the Gripen’s limit of just over 36,000 pounds. This capacity can be critical in mission scenarios requiring heavier armament.
In summary, both the F-16 Fighting Eagle and Gripen E are integral to their respective air forces, each offering unique strengths. The F-16, with its robust thrust capabilities and larger weapon capacity, contrasts with the Gripen’s impressive agility and multi-role design. As military needs evolve, the performance of these aircraft will continue to be under scrutiny, ensuring that they remain at the forefront of aerial combat technology.
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoIconic 90s TV Show House Hits Market for £1.1 Million
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoMilk Bank Urges Mothers to Donate for Premature Babies’ Health
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoAlessia Russo Signs Long-Term Deal with Arsenal Ahead of WSL Season
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoShoppers Flock to Discounted Neck Pillow on Amazon for Travel Comfort
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoMuseums Body Critiques EHRC Proposals on Gender Facilities
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoTrump Visits Europe: Business, Politics, or Leisure?
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoJapanese Teen Sorato Shimizu Breaks U18 100m Record in 10 Seconds
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoCouple Shares Inspiring Love Story Defying Height Stereotypes
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoAnglian Water Raises Concerns Over Proposed AI Data Centre
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoBournemouth Dominates Everton with 3-0 Victory in Premier League Summer Series
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoWreckage of Missing Russian Passenger Plane Discovered in Flames
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoShoppers Rave About Roman’s £42 Midi Dress, Calling It ‘Elegant’