Science
Scientists Detect Potential Evidence of Dark Matter After 90 Years
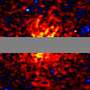
After almost a century of speculation, scientists may have uncovered direct evidence of dark matter, a mysterious substance that has eluded detection since it was first theorized. Using data from NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, researchers believe they have identified signs of this elusive matter, potentially allowing it to be “seen” for the first time.
Historical Context and Discovery
The concept of dark matter dates back to the early 1930s when Swiss astronomer Fritz Zwicky studied the motion of galaxies in the Coma cluster. Zwicky noticed that galaxies were moving at speeds that suggested they possessed far more mass than could be accounted for by visible matter alone. He hypothesized the existence of an unseen force, coining the term “dark matter” to describe this invisible scaffolding that holds galaxies together.
Despite numerous studies and indirect evidence over the decades, dark matter has remained undetected. The recent findings from the Fermi Observatory mark a significant advancement in the search for this cosmic enigma. Researchers have reported anomalies in gamma-ray emissions that may correlate with the presence of dark matter particles.
Significance of the Findings
The implications of this discovery are profound. If confirmed, these findings could reshape our understanding of the universe. Dark matter is believed to constitute approximately 27 percent of the universe’s total mass-energy content, while visible matter makes up only about 5 percent. The remainder is attributed to dark energy, a force driving the universe’s accelerated expansion.
Data gathered from the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope indicates unexpected gamma-ray signals from regions of space that are thought to be rich in dark matter. This evidence could potentially validate longstanding theories and help bridge gaps in our understanding of cosmic structure formation.
Researchers are urging caution, however, as the data requires further analysis. The scientific community is keenly aware of the need for rigorous validation before drawing definitive conclusions. The Fermi team is already planning additional observations to confirm the findings and rule out alternative explanations.
As scientists continue to analyze this promising data, the quest to uncover the nature of dark matter remains one of the most compelling challenges in modern astrophysics. If the presence of dark matter can indeed be confirmed, it would not only validate Zwicky’s early theories but also provide a crucial piece of the puzzle regarding the universe’s composition and evolution.
This potential breakthrough is a reminder of the enduring mystery of dark matter and the ongoing quest to understand the universe in its entirety. With advancements in technology and observational capabilities, the hope is that the next few years will yield more concrete evidence and bring us closer to understanding the invisible forces that shape our cosmos.
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoIconic 90s TV Show House Hits Market for £1.1 Million
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoMilk Bank Urges Mothers to Donate for Premature Babies’ Health
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoAlessia Russo Signs Long-Term Deal with Arsenal Ahead of WSL Season
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoShoppers Flock to Discounted Neck Pillow on Amazon for Travel Comfort
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoMuseums Body Critiques EHRC Proposals on Gender Facilities
-

 Business4 months ago
Business4 months agoTrump Visits Europe: Business, Politics, or Leisure?
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoJapanese Teen Sorato Shimizu Breaks U18 100m Record in 10 Seconds
-

 Politics4 months ago
Politics4 months agoCouple Shares Inspiring Love Story Defying Height Stereotypes
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoAnglian Water Raises Concerns Over Proposed AI Data Centre
-

 Sports4 months ago
Sports4 months agoBournemouth Dominates Everton with 3-0 Victory in Premier League Summer Series
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoWreckage of Missing Russian Passenger Plane Discovered in Flames
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoShoppers Rave About Roman’s £42 Midi Dress, Calling It ‘Elegant’









